Electronics automation is transforming industries across the globe. This technology streamlines processes and improves efficiency. It involves the use of electronics to control equipment and systems. From manufacturing to smart homes, electronics automation plays a crucial role.
Imagine a factory where machines work together. They communicate, adjust, and produce with minimal human intervention. This is the essence of electronics automation. It reduces errors and increases output. However, there are challenges to consider. Not all systems integrate seamlessly, leading to potential disruptions.
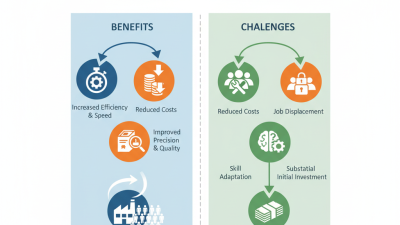
Businesses must reflect on their reliance on this technology. While the benefits are clear, automation can lead to job displacement. The balance between efficiency and employment is a significant concern. Embracing electronics automation requires careful thought and planning.

Electronics automation refers to the use of electronic systems to control and manage processes. It plays a pivotal role in various industries. Essentially, it combines hardware and software to automate repetitive tasks, improving efficiency and accuracy. For example, assembly lines in manufacturing often use sensors and controllers to streamline production. This integration reduces human error and saves time. However, one must consider the potential for system failures and the complexity that comes with advanced setups.
In the realm of electronics automation, several key concepts are essential. Sensors collect real-time data about an environment. Actuators respond to this data, executing commands based on predetermined criteria. For instance, a temperature sensor might trigger a cooling system when it detects a rise in heat. This creates a responsive system. Still, challenges like sensor malfunctions can disrupt operations. The reliance on automated systems raises concerns about job displacement too. Balancing efficiency with ethical considerations remains a crucial discussion in the field of electronics automation.
| Aspect | Description | Key Technologies | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronics automation refers to the use of electronic devices and systems to automate various tasks and processes. | Microcontrollers, PLCs, Sensors, Actuators | Manufacturing, Home Automation, Robotics |
| Key Components | Central processing unit (CPU), Input/output devices, Power supply | Embedded Systems, Control Systems, Networking | Industrial Control, Smart Grids |
| Benefits | Increased efficiency, Reduced human error, Cost savings over time | IoT Devices, AI Integration, Data Analytics | Healthcare, Agriculture, Smart Homes |
| Challenges | High upfront costs, Security risks, Dependence on technology | Cybersecurity Solutions, System Integration Tools | Quality Control, Predictive Maintenance |
Electronics automation has transformed various industries by enhancing efficiency and precision. In manufacturing, automated systems control machinery, reducing the likelihood of human error. These systems can operate 24/7, increasing production rates and lowering costs. Imagine a factory where robots assemble products flawlessly, while data analytics monitors their performance in real-time. This integration speeds up processes, but can also lead to over-reliance on technology.
In sectors like healthcare, electronics automation plays a crucial role in patient management. Automated systems handle scheduling and record-keeping, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care. However, this reliance on tech can create vulnerability. A single malfunction might disrupt operations, leading to delays in critical services. Furthermore, constant automation might reduce essential human interactions, possibly affecting patient experience.
The impact of electronics automation isn't flawless. While it streamlines tasks, it can lead to job displacement in some areas. Workers may feel uncertain about their roles. The challenge lies in balancing technology and human skills. Industries must reflect on these issues. Embracing innovation is vital, but the human element remains irreplaceable.
Electronics automation is revolutionizing many industries today. Several key components facilitate this transformation. Sensors play a vital role, collecting data from their environment. They can detect changes in temperature, light, and pressure. This data is then used to make informed decisions.
Microcontrollers are another essential component. They act as the brain of automated systems. They receive input from sensors and control outputs accordingly. This interconnectedness creates a seamless operation. However, not all systems work flawlessly; occasional glitches can occur. These can lead to a cycle of trial and error during the development phase.
Communication technologies, such as IoT, enhance automation. They allow devices to connect and share information. But, integrating these systems can be complex. Sometimes, compatibility issues arise. It’s essential to address these challenges for successful implementation. With continuous innovation, the future of electronics automation looks promising. Yet, ongoing adjustments and refinements will be necessary to achieve optimal performance.
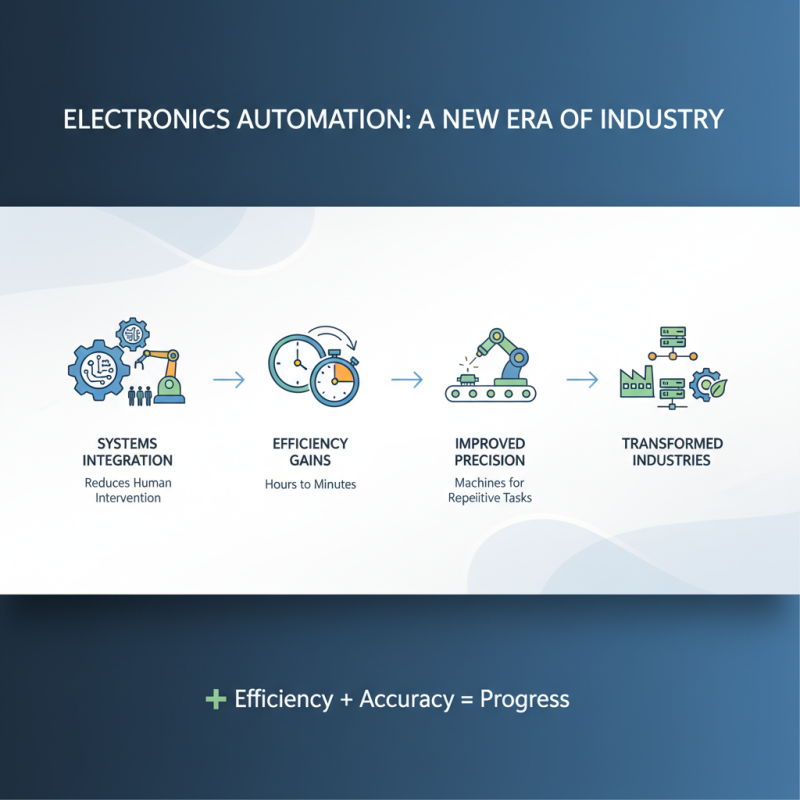
Electronics automation has transformed various industries. It integrates systems that reduce human intervention. This shift leads to notable efficiency gains. Tasks that once took hours can now be done in minutes. Precision in manufacturing improves as machines take over repetitive tasks.
However, the transition is not without challenges. Implementing automation requires significant investment. Training staff to adapt to new technologies can be overwhelming. Some workers may resist change, fearing job loss. Yet, these challenges can lead to a more skilled workforce.
The benefits of automation often outweigh the downsides. Companies report a drop in error rates. Production lines run smoother with less downtime. Overall, the focus on efficiency and precision is reshaping our approach to various tasks. Embracing these changes can open doors to new opportunities.
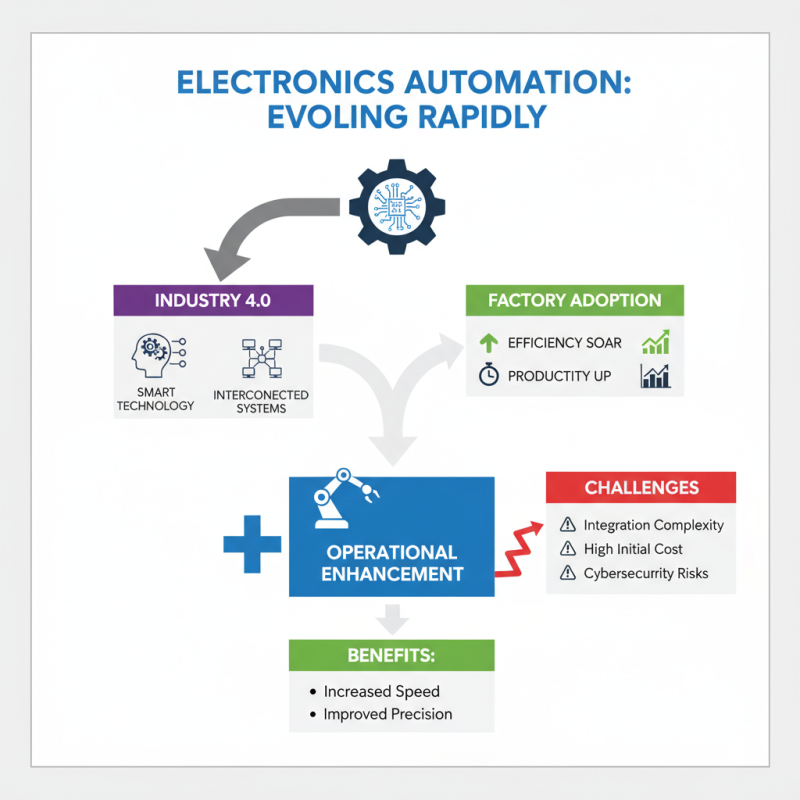
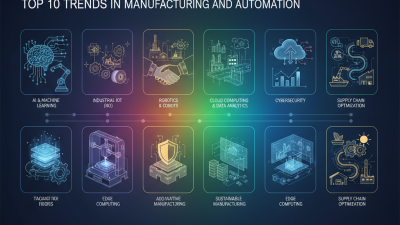
Electronics automation is evolving rapidly. It plays a crucial role in Industry 4.0. This new industrial era focuses on smart technology and interconnected systems. As factories adopt these technologies, efficiency and productivity soar. Automation enhances operations, but not without challenges.
One key trend is the integration of AI into electronics automation. AI can analyze data in real-time, improving decision-making. Machine learning algorithms adjust processes automatically. However, companies must invest in training. There’s a skill gap in many industries. New technology requires skilled workers. Encourage employees to embrace ongoing education.
Tip: Implement small pilot projects before scaling automation. This approach helps identify potential pitfalls early. Regular feedback from team members can improve project outcomes. Also, don't overlook cyber-security. Increased automation means more entry points for cyber threats. Organizations need robust security measures to protect sensitive data. Embracing these changes is essential, but reflection on their impacts remains vital. The journey towards full integration is complex. Balance ambition with practicality for successful transitions.