In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, the concept of "full automation" is emerging as a transformative force that promises to reshape industries and improve operational efficiency. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, as many as 45% of the activities workers perform can be automated using currently available technologies. This statistic highlights the potential for businesses to leverage full automation to streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. As organizations increasingly turn to automation solutions, the integration of artificial intelligence and robotic process automation (RPA) is proving to be a game-changer.
Furthermore, a study by PwC estimates that by 2030, up to 30% of jobs could be automated, leading to a significant shift in the workforce landscape. This shift not only affects job roles but also necessitates a strategic rethinking of business models. Companies embracing full automation can gain a competitive edge, responding quicker to market demands and reallocating human resources to higher-value tasks. As we delve deeper into the implications of full automation, it becomes evident that its adoption is not just a trend, but a critical strategy for future-proofing businesses in an increasingly digital world.

Full automation refers to the use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention, transforming how businesses operate across various industries. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, by 2030, up to 800 million jobs could be displaced by automation, but it also opens the door for significant productivity gains. Full automation integrates advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency. Companies can automate routine processes such as data entry, inventory management, and customer service, allowing human employees to focus on more strategic, value-added activities.
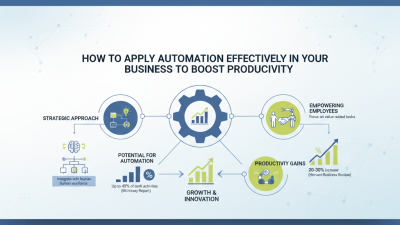
The scope of full automation extends beyond mere task execution; it encompasses the entire workflow of a business. A study by the World Economic Forum highlighted that companies adopting automation technologies have reported productivity increases ranging from 20% to 30%. Moreover, automation drives consistency in output quality and speeds up production cycles. Industries including manufacturing, healthcare, and finance have started to leverage automation not only to cut costs but also to refine their service delivery, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction. Engaging with automation can redefine operational effectiveness, resulting in agile and resilient businesses capable of thriving in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
This bar chart illustrates the projected increase in productivity due to full automation over five years. As businesses adopt automation technologies, they can expect significant growth in efficiency and output.
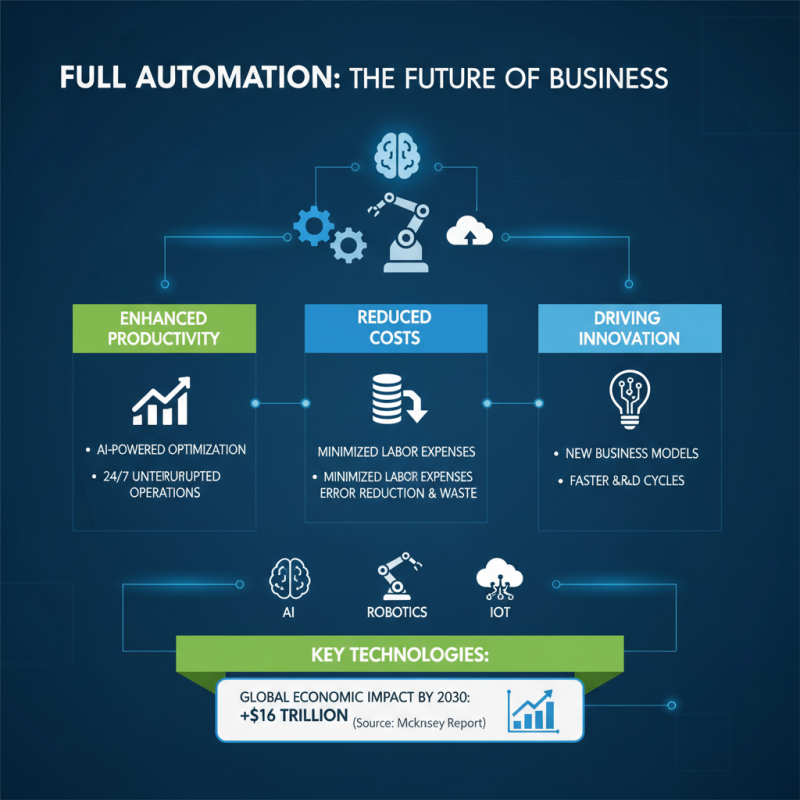
Full automation represents a significant leap forward for businesses across various industries, enabling them to enhance productivity, reduce operational costs, and drive innovation. Key technologies powering this transformation include artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). According to a report by McKinsey, automation could increase global productivity by up to 1.4% annually, which can lead to a cumulative economic impact of $16 trillion by 2030.
In manufacturing, robotics is at the forefront of full automation, with the International Federation of Robotics noting that service robots can reduce labor costs by approximately 30%. These robots streamline production lines, minimize human error, and can operate 24/7 without the risk of fatigue. Furthermore, the integration of IoT devices allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime by up to 50%, as highlighted in a study by Deloitte.
In sectors like logistics and healthcare, automation technologies such as AI-driven analytics and autonomous vehicles are revolutionizing operations. Research by Gartner indicates that AI adoption in supply chain management can enhance demand forecasting accuracy by 75%, leading to better inventory management and decreased excess stock. Meanwhile, in healthcare, robotic process automation is projected to save the industry over $150 billion annually by improving administrative efficiencies and allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care rather than administrative tasks.
Full automation represents a significant leap in technology, enabling businesses to streamline their operations by integrating advanced systems and robotics that perform repetitive tasks without human intervention. One of the most profound impacts of full automation is its potential to elevate operational efficiency. By automating routine processes such as inventory management, data entry, and customer support, companies can minimize human error and increase speed, ultimately allowing employees to focus on more strategic tasks that drive innovation and growth.
Cost reduction is another critical benefit of full automation. Organizations can achieve considerable savings by reducing labor costs and minimizing resource wastage. Automation optimizes resource allocation, ensuring that materials and time are used effectively. In industries such as manufacturing and logistics, automated systems can operate around the clock, significantly enhancing productivity levels while decreasing overhead costs. Consequently, businesses can offer competitive pricing and improved service delivery, solidifying their market position. By embracing full automation, companies not only streamline their operations but also pave the way for sustainable growth in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
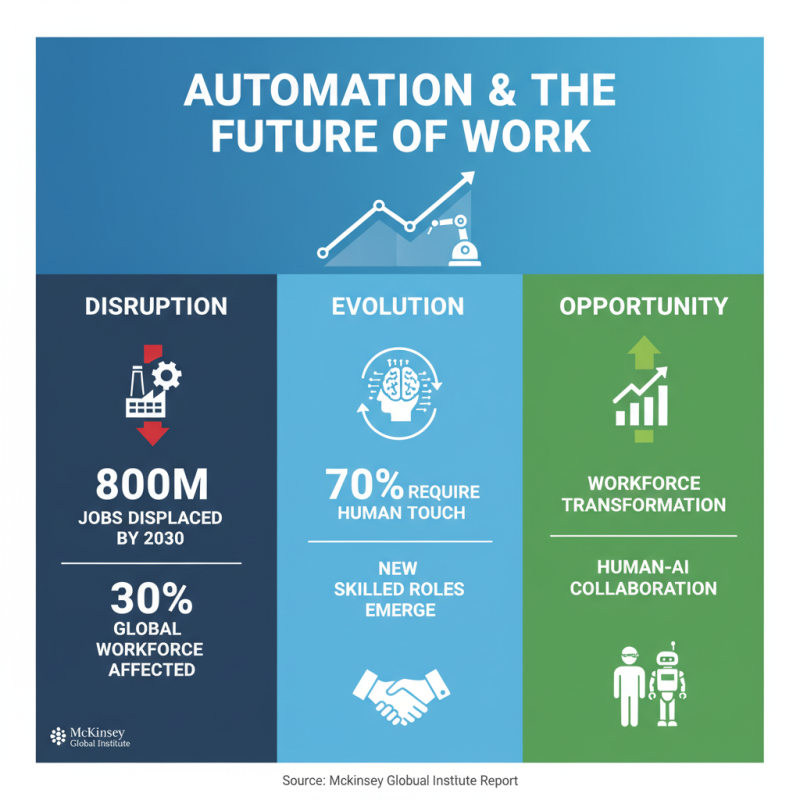
The rise of full automation is reshaping the workforce landscape significantly. According to a report by McKinsey Global Institute, up to 800 million jobs worldwide could be displaced by automation by 2030, affecting almost 30% of the global workforce. However, this shift also presents an opportunity for workforce transformation, as many industries adapt to new technologies and roles evolve or emerge. The same report indicates that while one-third of tasks can be automated, it also implies that 70% of current jobs will have elements that necessitate a human touch, leading to an increased demand for skilled professionals who can work alongside automated systems.
Statistics from the World Economic Forum further highlight this transformation. By 2025, it's projected that 85 million jobs may be displaced by a shift in labor between humans and machines. Conversely, the adoption of automation may create 97 million new roles, particularly in fields such as data analysis, artificial intelligence management, and digital communication. This is a clear indicator that businesses embracing full automation can not only enhance operational efficiency but also drive job creation in new sectors, fostering a more adaptable and skilled workforce prepared for the future.
Full automation has emerged as a revolutionary force in various industries, as evidenced by successful case studies that demonstrate its transformative potential. For instance, a manufacturing company implemented a fully automated assembly line, which not only drastically reduced production time but also minimized errors typically associated with manual labor. By integrating advanced robotics and artificial intelligence, the company achieved a significant increase in output while maintaining high-quality standards. This shift allowed for resource reallocation, enabling the workforce to focus on more strategic tasks.
In the retail sector, a prominent chain adopted full automation for its inventory management system. Using real-time data analytics and automated reordering processes, the business minimized stock shortages and excess inventory, leading to improved cash flow and customer satisfaction. This case underscores how automation can streamline operations, reduce operational costs, and enhance the overall shopping experience. Such successful implementations illustrate that full automation is not merely about replacing human labor; it represents a profound shift in operational efficiency and strategic focus, paving the way for innovative practices across various sectors.