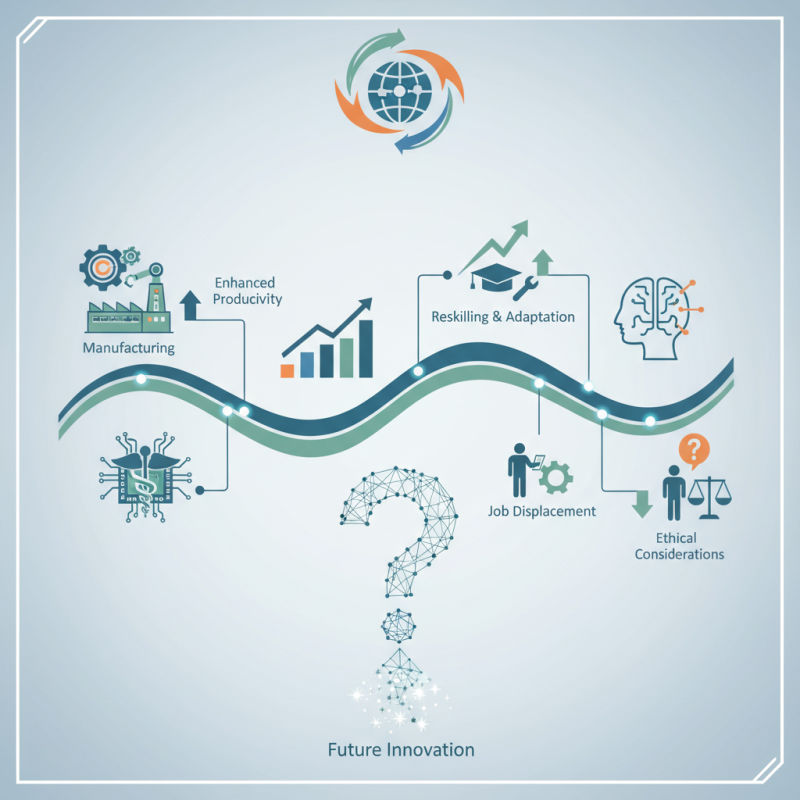
As we look ahead to 2026, the landscape of technical automation is rapidly evolving. Businesses are increasingly investing in automated systems to enhance productivity. This shift affects various industries, from manufacturing to healthcare, where precision and efficiency are pivotal. Technical automation introduces advanced algorithms and robotics, reshaping traditional workflows.
However, the rise of technical automation isn't without challenges. Job displacement looms as machines take over tasks previously handled by humans. Companies must carefully navigate the balance between efficiency and the workforce’s well-being. There’s a growing need for reskilling and adapting to this technological shift. Not every implementation of technical automation yields positive results; setbacks and failures are common.
Moreover, ethical considerations arise as systems become more autonomous. Questions about accountability and decision-making in automated settings remain. Addressing these concerns is crucial as we embrace the future. The trajectory of technical automation in 2026 will depend on how society confronts these challenges and leverages the potential for innovation.
The future of technical automation is evolving rapidly. By 2026, we expect to see significant advancements. Many industries will embrace automation to boost efficiency and reduce costs. Automation will touch various sectors, from manufacturing to healthcare. Workers may need to adapt, as jobs change and evolve.
While automation offers many benefits, there are concerns. Some fear job displacement. Certain tasks may become obsolete. This raises questions about retraining and upskilling workers. Companies must consider the human impact of their automation choices. Not every task should be automated.
As we look towards 2026, the landscape of automation technologies is set to evolve dramatically across global industries. Many sectors are embracing automation to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Manufacturing, for example, is adopting robotic systems for faster production. These machines perform tasks with precision, yet reliance on automation raises questions about workforce displacement.
In the services sector, AI-driven tools are transforming customer interactions. Companies are utilizing chatbots and virtual assistants for support. While these innovations improve service speed, they can sometimes lack the human touch, leading to unsatisfactory customer experiences. The balance between efficiency and empathy needs careful consideration.
Industries are projected to invest heavily in automation, but challenges lurk in the shadows. Skills gaps may widen, leaving some workers behind. Not everyone has access to training programs. As we advance, the ethical implications of automation must be addressed. Creating a future where technology serves everyone requires deliberate action and thoughtful strategies.
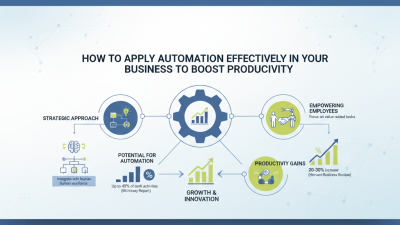
The landscape of automation is evolving rapidly. By 2026, AI and machine learning are set to redefine automation processes across various sectors. According to a recent report by McKinsey, companies that implement AI-driven automation could see a productivity boost of up to 40%. This shift could lead to significant changes in workforce dynamics and operational strategies.
AI technologies automate tasks that were once labor-intensive. This automation helps in data analysis and customer service, increasing efficiency. However, these advancements also bring challenges. A report by PwC indicates that around 30% of jobs could be automated by 2030. The fear of job displacement is palpable. Companies must balance efficiency gains with the need for human talent, requiring ongoing training and development.
Machine learning algorithms are becoming more sophisticated. Yet, they are not without flaws. Bias in AI models can lead to inaccurate decisions. This situation demands ongoing oversight. Addressing these issues will be crucial as we move into a future dominated by technical automation. Emphasizing ethical practices alongside technological advances will shape successful automation strategies moving forward.
This chart illustrates the projected percentage of automated processes across various industries by 2026 as influenced by AI and Machine Learning technologies.
As we look ahead to 2026, automation is expected to reshape various industries. The manufacturing sector is at the forefront of this transformation. A study by McKinsey predicts that up to 61% of manufacturing tasks could be automated by then. This shift promises increased efficiency but raises concerns about workforce displacement. Job roles that require manual labor will be significantly impacted.
Healthcare is another industry embracing automation. According to a report from Deloitte, automation could save the healthcare sector up to $50 billion annually by 2026. Tasks such as patient data management and appointment scheduling are increasingly being handled by automated systems. However, such reliance on technology poses risks. Challenges include maintaining data privacy and ensuring reliable patient care.
The logistics and supply chain industry is not far behind. A recent report from Accenture highlights that automation could reduce supply chain costs by 30% by 2026. Robots and AI-powered analytics are optimizing inventory management and delivery processes. Yet, with this advancement comes complexity. Companies must evaluate their readiness for such a dramatic change and plan for necessary workforce training.
| Industry | Predicted Automation Adoption Rate (%) | Key Technologies Driving Automation | Projected Cost Savings (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 75% | AI, Robotics, IoT | 20% |
| Healthcare | 65% | Telemedicine, AI Diagnostics | 15% |
| Finance | 80% | Robotic Process Automation, Blockchain | 25% |
| Retail | 70% | Automated Checkout, Inventory Management Systems | 18% |
| Transportation | 68% | Autonomous Vehicles, AI Traffic Management | 22% |
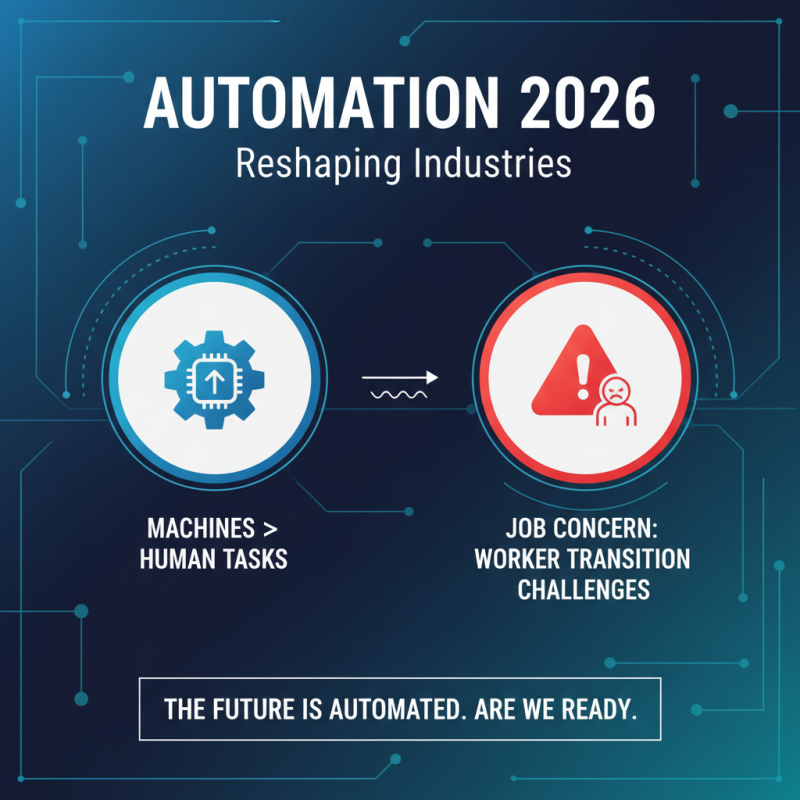
As we approach 2026, technical automation is set to reshape industries. Many jobs will be affected, raising concerns among workers. What happens when machines take over tasks previously done by humans? This transition poses real challenges.
Workers must adapt to new technologies. Upskilling becomes essential. However, not everyone has access to training programs. Some may feel left behind. The gap between skilled and unskilled workers could widen. This creates both fear and opportunity.
Moreover, industries must reflect on ethical implications. Automation can enhance productivity but may also reduce job satisfaction. Workers may face increased pressure to perform. Balancing efficiency with human needs is crucial. As we step into this new era, we must navigate these complexities mindfully.