In today’s rapidly evolving landscape, technology automation has emerged as a driving force behind significant industry transformations. As businesses integrate automation, they improve efficiency and reduce costs. However, these changes come with challenges that need attention.
Take, for example, the healthcare sector. Automation streamlines patient data management, yet it raises concerns about data privacy. Companies must balance efficiency with ethical considerations. In manufacturing, robots enhance production, but they also pose questions about job displacement and the future workforce. This highlights the need for thoughtful implementation in technology automation.
Moreover, in the retail industry, automation optimizes inventory management and enhances customer experience. Yet, it challenges traditional retail models and demands adaptability. As industries embrace technology automation, understanding both its benefits and drawbacks is crucial for sustainable growth.

The rise of artificial intelligence is reshaping automation processes across various industries. AI technologies streamline workflows. Machine learning enables systems to learn from data, improving accuracy and efficiency. For instance, AI can predict maintenance needs in manufacturing. This anticipatory approach reduces downtime and saves costs. Yet, reliance on algorithms poses risks. If the data is biased, it could lead to flawed decision-making.
In customer service, AI chatbots handle inquiries 24/7. They provide instant responses and can analyze customer sentiment. However, they sometimes lack empathy and may frustrate users. There’s a fine line between efficiency and personal touch. Businesses must find a balance to ensure customer satisfaction. The potential for AI in automation is immense, but it is not without challenges. Companies must continually assess the impact of these technologies on their operations and workforce. Adaptation is key to harnessing the full benefits of AI-driven automation.
The integration of robotics into manufacturing and supply chains is reshaping how industries operate. Robots are taking over repetitive tasks. This change boosts productivity and reduces labor costs. In factories, robotic arms assemble products with precision. They work tirelessly, minimizing errors. However, reliance on technology raises questions about job displacement.
In supply chains, autonomous vehicles and drones deliver goods faster. These innovations improve efficiency and speed. But, they also require significant investment. Many companies struggle with the initial costs. Upgrading existing systems can be a challenge. Not every business can adapt quickly.
As robotics become more prevalent, human roles are changing. Workers may need to learn new skills. This shift might lead to job loss in some sectors. Yet, new opportunities arise in tech and maintenance. The balance between automation and employment needs careful consideration. Companies must reflect on their operational strategies.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping automation and data management. Many industries are embracing connected devices, allowing for real-time data collection. Factories equipped with sensors monitor equipment health continuously. This provides valuable insights into performance. Businesses can predict failures before they happen. Automation reduces downtime and boosts efficiency.
However, with the rise of IoT, data management becomes more complex. Companies must handle vast amounts of data. Not all data collected is useful. Distinguishing valuable insights from noise can be challenging. Some organizations struggle with integration. They may find their systems incompatible, leading to inefficiencies.
Moreover, security risks are a significant concern. Increased connectivity can expose vulnerabilities. Data breaches can have severe repercussions. Companies must invest in robust security measures. Educating employees on these risks is crucial. Despite the challenges, the potential benefits of IoT in automation are immense. Adapting to this shift requires thoughtful strategy and continual improvement.
| Trend | Description | Impact on Industries | Data Management Innovations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Leveraging AI for predictive analytics and automation | Improving operational efficiency across sectors | Enhanced data processing and analysis |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Connecting devices for real-time analytics | Transforming supply chains and logistics | Real-time data collection and integration |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | Automation of repetitive tasks | Reducing labor costs and minimizing errors | Streamlined data entry and retrieval processes |
| Cloud Computing | Flexible resource scaling and data storage solutions | Facilitating remote work and collaboration | Improved data security and backup solutions |
| Blockchain | Decentralized data management and security | Enhancing transparency and trust in transactions | Immutable records and data sharing |
| Augmented Reality (AR) | Integrating digital information into the physical world | Revolutionizing training and real-time assistance | Enhanced visualization of data |
| Voice Assistants | Using voice commands to automate tasks | Improving user accessibility and interaction | Voice-activated data entry |
| Predictive Maintenance | Forecasting equipment failures before they occur | Minimizing downtime across industries | Data-driven maintenance scheduling |
| 5G Technology | High-speed internet enabling faster data transmission | Supporting smart cities and autonomous vehicles | Real-time data processing capabilities |
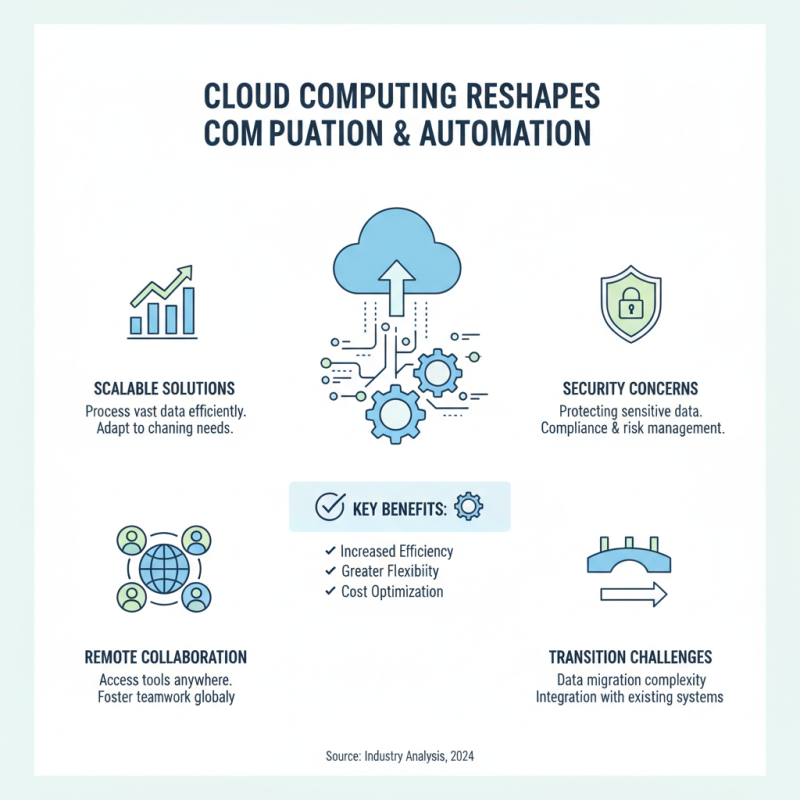
The rise of cloud computing is reshaping the automation landscape across industries. Organizations now leverage cloud platforms for scalable solutions. This shift enables them to process vast amounts of data efficiently. Teams can now access their tools and applications from anywhere, fostering remote collaboration. However, adopting cloud solutions is not without challenges. Transitioning can lead to security concerns, especially if sensitive data is involved.
Many companies face difficulties in integrating existing systems with new cloud technologies. This can cause delays and increase operational costs. Training staff to use these new systems also requires time and resources. Despite these hurdles, the potential benefits of cloud-powered automation are significant. Organizations must weigh the advantages against the risks to make informed decisions. Ultimately, cloud computing opens doors to endless possibilities, pushing industries into a new era of efficiency.
The evolution of automation in service industries is reshaping customer experiences.
Intelligent chatbots now handle inquiries, offering quick responses. Yet, they can't replicate human empathy. Some customers feel frustrated when they encounter machines instead of people.
Self-service kiosks and mobile apps are gaining popularity. They streamline transactions and enhance efficiency. However, many users struggle with technology. Older customers may feel left out. This gap raises questions about accessibility and inclusivity. Businesses must balance efficiency with personal touch.
Data analytics play a significant role in enhancing customer experiences. They provide insights into preferences, creating tailored services. Despite advantages, companies face challenges in data privacy. Customers often worry about how their information is used. Striking a balance between personalization and security is crucial for success.