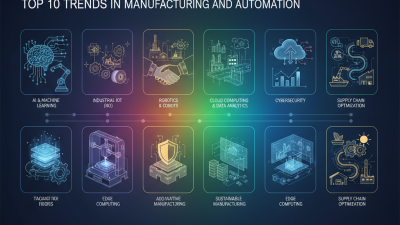
In 2026, the landscape of manufacturing and automation is set for radical changes. Innovations are emerging, reshaping how industries operate. The focus is on efficiency, speed, and sustainability. Companies are adopting cutting-edge technologies like IoT and AI for better decision-making.
As manufacturing and automation evolve, challenges accompany advancements. Workforce adaptation is crucial. Skills may lag behind technological growth. Furthermore, high costs of implementation could deter smaller businesses. However, innovation must persist to remain competitive.
A balanced approach could lead to breakthroughs. Collaborative robots are a promising trend. They augment human capabilities while ensuring safety. These innovations carry the potential to redefine productivity. The path ahead is exciting yet requires careful navigation of its pitfalls.


Emerging technologies are reshaping the manufacturing landscape in 2026. According to a recent industry report, advanced robotics and artificial intelligence are being integrated at unprecedented rates. These innovations enable higher precision, reducing waste by up to 30%. However, the learning curve can be steep. Many companies struggle to adapt their workforce to new automation processes.
Another key trend is the rise of smart factories. IoT devices are being employed to enhance real-time data collection. This move allows for better predictive maintenance, extending machine lifespan by an average of 25%. Yet, the reliance on digital solutions poses cybersecurity risks that must not be overlooked. As firms invest in technology, some neglect to fortify their digital defenses.
Sustainability remains a concern. The push for greener manufacturing practices is growing. Reports indicate that over 60% of manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials and processes. However, many are faced with compliance challenges and may feel overwhelmed by the complexity. Competing on sustainability while keeping costs manageable is an ongoing battle for many in the sector.
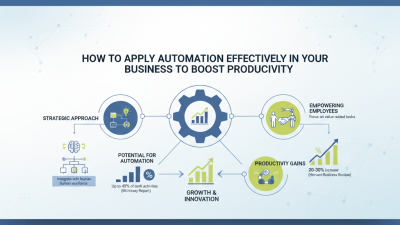
The rise of AI and machine learning is revolutionizing automation techniques in manufacturing. With smart algorithms, machines can now learn from vast amounts of data. This leads to better decision-making and predictive maintenance. For example, AI can analyze patterns in machine performance, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
Tips for integrating AI into your automation processes:
While the potential is vast, challenges exist. Not all AI systems are created equal. Some may not align with specific manufacturing needs. It’s important to remain flexible. Understand that adjustments might be necessary. Strive to find the right balance between human oversight and machine learning capabilities.
Sustainability is reshaping manufacturing like never before. Companies are prioritizing eco-friendly materials and energy efficiency. This shift reflects a growing commitment to reduce environmental footprints. Factories are transitioning to renewable energy sources. Solar panels and wind turbines are becoming common sights.
Innovations in automation are also aligning with sustainability goals. Smart technologies optimize energy use and minimize waste. Sensors track resource consumption in real-time. Yet, many organizations struggle to implement these technologies. High costs and integration challenges often hinder progress.
A focus on circular economy principles is emerging. This means designing products with recyclability in mind. However, challenges remain. Employees need training, and supply chains must adapt. Sustainable manufacturing is a journey, not a destination. Companies are learning, evolving, and making mistakes along the way.
| Trend | Description | Impact on Sustainability | Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Circular Manufacturing | Emphasizes recycling and reusing materials to reduce waste. | Reduces landfill waste and encourages resource efficiency. | 70% |
| Smart Automation | Utilizes AI and IoT to optimize manufacturing processes. | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces carbon footprint. | 65% |
| Additive Manufacturing | 3D printing technology to create products layer by layer. | Minimizes material waste and energy consumption. | 50% |
| Energy Management Systems | Systems to monitor and optimize energy usage in factories. | Reduces energy costs and carbon emissions. | 75% |
| Sustainable Supply Chain | Focuses on sourcing materials responsibly and ethically. | Promotes ethical practices and reduces environmental impact. | 60% |
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in smart manufacturing systems is transforming the industry. By 2026, it's expected that smart factories will grow by around 30%, greatly benefiting from IoT technologies. These systems allow for real-time data acquisition and analysis, enhancing production efficiency and quality. However, the complexity of such integration poses significant challenges.
Many manufacturers face hurdles when implementing IoT solutions. Legacy systems often lack compatibility with new technologies. This results in fragmented data and inefficient operations. A report reveals that nearly 70% of manufacturers struggle with integration. Additionally, security remains a pressing concern. As machines become interconnected, they become more vulnerable to cyber threats. Companies must address these issues to fully harness IoT's potential.
Despite these challenges, the rewards can be substantial. Enhanced predictive maintenance through IoT can reduce downtime by up to 50%. Real-time monitoring enables firms to respond quickly to production issues. However, achieving seamless integration requires ongoing investment and training. The journey toward a fully integrated smart manufacturing system is complex but essential for staying competitive in the market.
As manufacturing embraces automation, the workforce landscape is changing dramatically. Workers need to shift their focus from traditional skills to new competencies. Strong digital literacy is vital. Employees must understand data analytics, robotics, and artificial intelligence. Some may find it overwhelming. The rapid pace of change can be intimidating. But adaptability is key.
Collaboration will also play a crucial role. Workers must learn to work alongside automated systems. This requires a combination of technical knowledge and interpersonal skills. Problem-solving will become increasingly important. Teams will face challenges with technology that are unpredictable. The ability to think critically will be essential in navigating these hurdles.
Moreover, continuous learning must become a habit. Online courses and workshops can fill skills gaps. However, not everyone has easy access to resources. This disparity could hinder progress for some. Organizations should invest in training programs. Fostering a culture of growth and improvement can drive success in this evolving environment. Without proactive efforts, the workforce may struggle to keep pace with automation.